 |
VIRTUALFIELD TRIP TO THE KEWEENAW PENINSULA, MICHIGAN - STRUCTURE
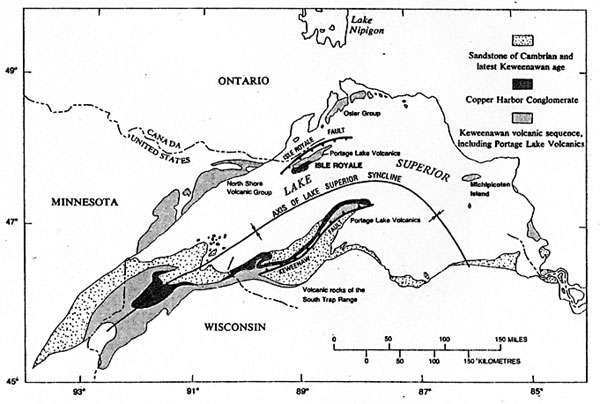
The Keweenaw peninsula is bisected by the Keweenaw fault, which is the boundarybetween the mid continent rift and other Precambrian terrains. Lake Superior isthe result of a combination of a geological syncline which helped form astructural basin that has been subsequently enhanced by the actions of glaciers whichexcavated the softer rocks which previously occupied the middle of the syncline.
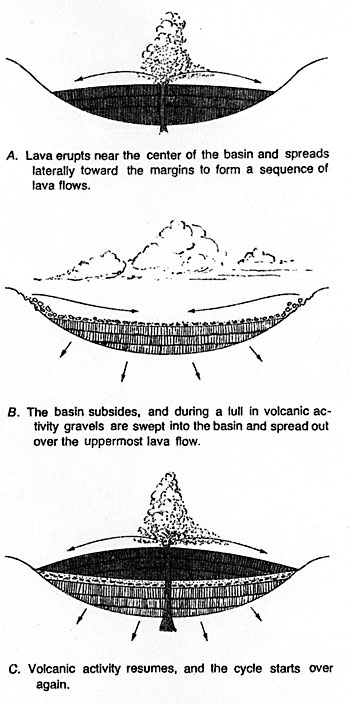
The midcontinent rift (Precambrian in age) starts in northern Kansas and runs under Lake Superior andthen turns south to run through lower Michigan. It was similar to the East Africa rift as parts of the continent tried toseparate, but were ultimately unsuccessful in the attempt to break into separateland masses. As the rift developed, there weretwo bounding graben faults at either side of the rift, the Keweenaw fault on theeastern side of the rift and the Isle Royale fault on the western edge of therift. As the rocks were beingdown-warped, igneous extrusions filled the rift valley. These eruptions werealmost exclusively on dry land ( there is one location on the Keweenaw peninsulaand several small areas on Isle Royale that were erupted under water - as seenin the development of pillow lavas). During periods of volcanic quiescence, thedown-warping continued and sedimentary rocks were formed from the erosion of thesurrounding higher land areas.
TheKeweenaw is the eastern flank of a large syncline under Lake Superior, while therock outcrops on Isle Royale represent the western flank of the syncline. Mostof the rocks generally dip about 20 degrees to the west on the Keweenawpeninsula. There are minor gentle folds, synclines and anticlines that haveamplitudes extending over 10 km distances in the Keweenaw thatalong with cross faults, tend to provide pathways for the copper ore solutionsand localize the deposition of native copper. The Allouez gap fault provided the mostproductive pathway through the volcanics. More rock formations were mineralized next tothis fault than any other structure in the Keweenaw.
About 30 million years after the rift formed, the region was placed undercompression by the northwest movement of the plate along the Grenville front (this is located several hundred miles to the southeast). This compressionresulted in the normal graben faults becoming reverse faults. Although theKeweenaw fault is present throughout the length of the peninsula, it is poorlyexposed along it's entire length. |
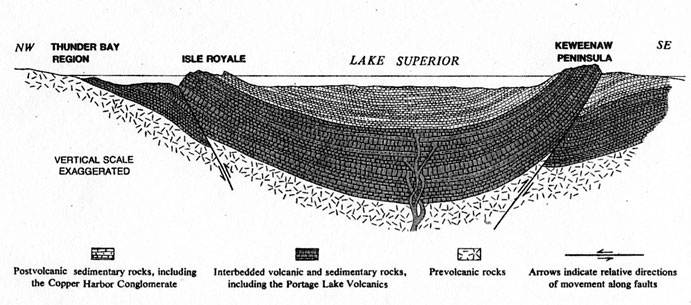
A cross section of the Lake Superior basin from Thunder Bay Canada, through IsleRoyale and to the Keweenaw peninsula. From USGS Bulletin 1309, figure 38.
| [Include:'../../../inc/footer.html'] |